1. Overview
A brain aneurysm is a bulge or "ballooning" in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. A small aneurysm often causes no symptoms. But if it grows, an aneurysm can press on nerves inside your brain, causing pain and other symptoms. It can also leak blood or burst, causing a sudden, severe headache.
A burst aneurysm is a very serious, life-threatening emergency that needs to be treated right away. It leads to a bleeding (hemorrhagic) stroke. Stroke is the term doctors use when a part of the brain is damaged because of a problem with blood flow. The stroke that happens after a brain aneurysm bursts is called a "subarachnoid hemorrhage."
2. Risk Factors
◆ Behavioral: hypertension, cigarette smoking, alcohol abuse, drugs such as cocaine
◆ Gender (female 1.24 times higher than men)
◆ History of cerebral aneurysm
◆ Family history of aneurysms
◆ Genetic syndromes (autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
3. Presentations
◆ Headache. Usually severe (classic description: “the worst headache of my life”) and sudden in onset (paroxysmal)
◆ Stiff neck
◆ Passing out
◆ Nausea and vomiting
◆ Sensitivity to light
◆ Blurred or double vision and a drooping eyelid
4. Examinations
◆ Imaging tests – These tests include a CT scan and an MRI. Both show pictures of your brain. During these tests, you might also get an injection of a dye that makes it easier for doctors to see blood flow in the brain.
◆ Lumbar puncture (sometimes called a "spinal tap") – During this procedure, a doctor puts a needle into your lower back and takes out a small sample of spinal fluid. Spinal fluid is the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. If this fluid has more red blood cells than usual, you could have a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
◆ Cerebral angiogram – For this test, your doctor puts a thin, plastic tube into a large blood vessel, usually near the top of your thigh. Then they will advance the tube through your blood vessels past your heart to your brain. Your doctor then injects dye that shows up on an X-ray. This lets the doctor see the blood vessels in your brain and find the aneurysm.
5. Surgical Treatment Options
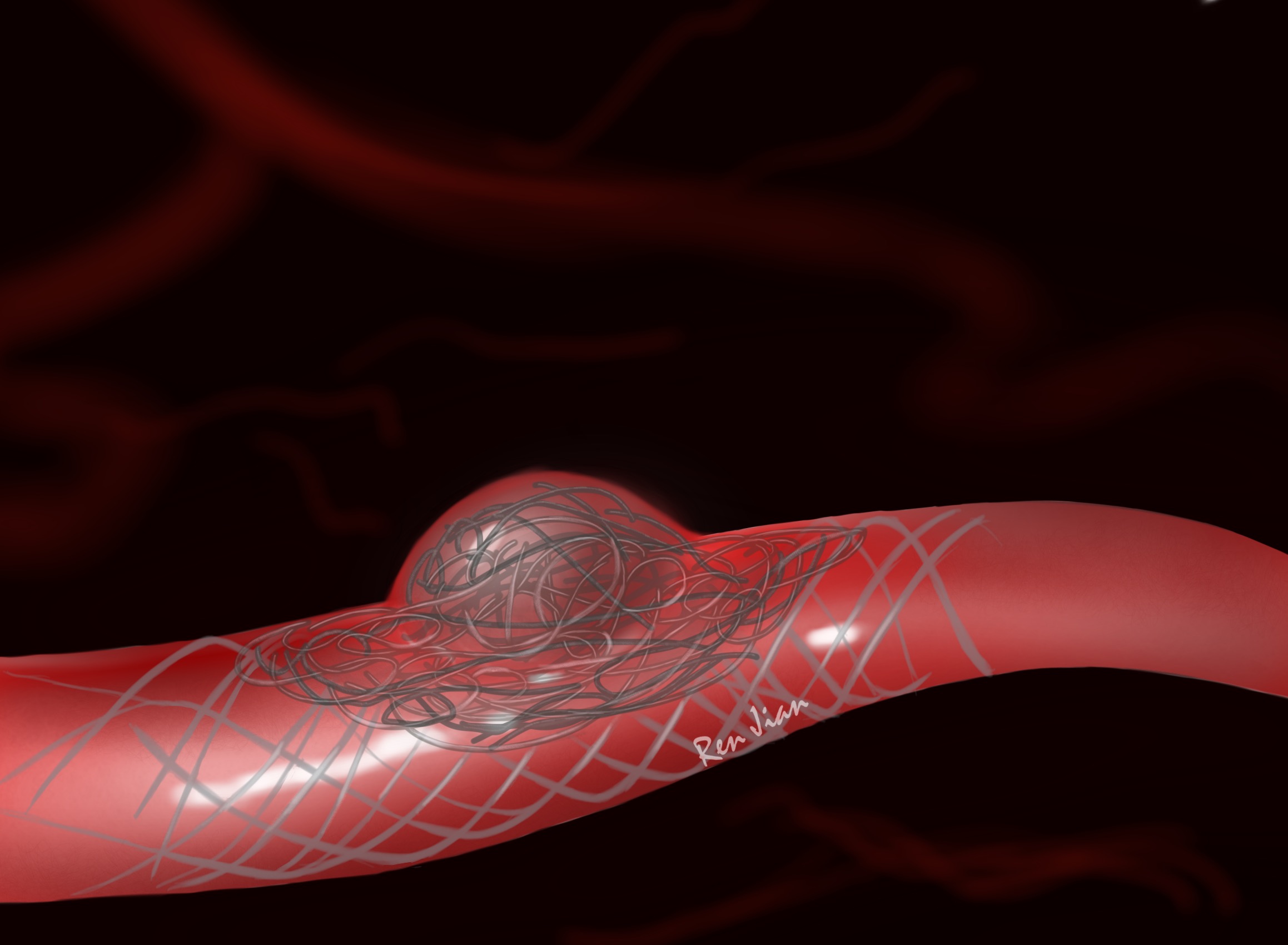
◆ Coil embolism
This is endovascular treatment. Your doctor inserts coils into the lumen of the aneurysm endovascularly. A local thrombus then forms around the coils, obliterating the aneurysmal sac.
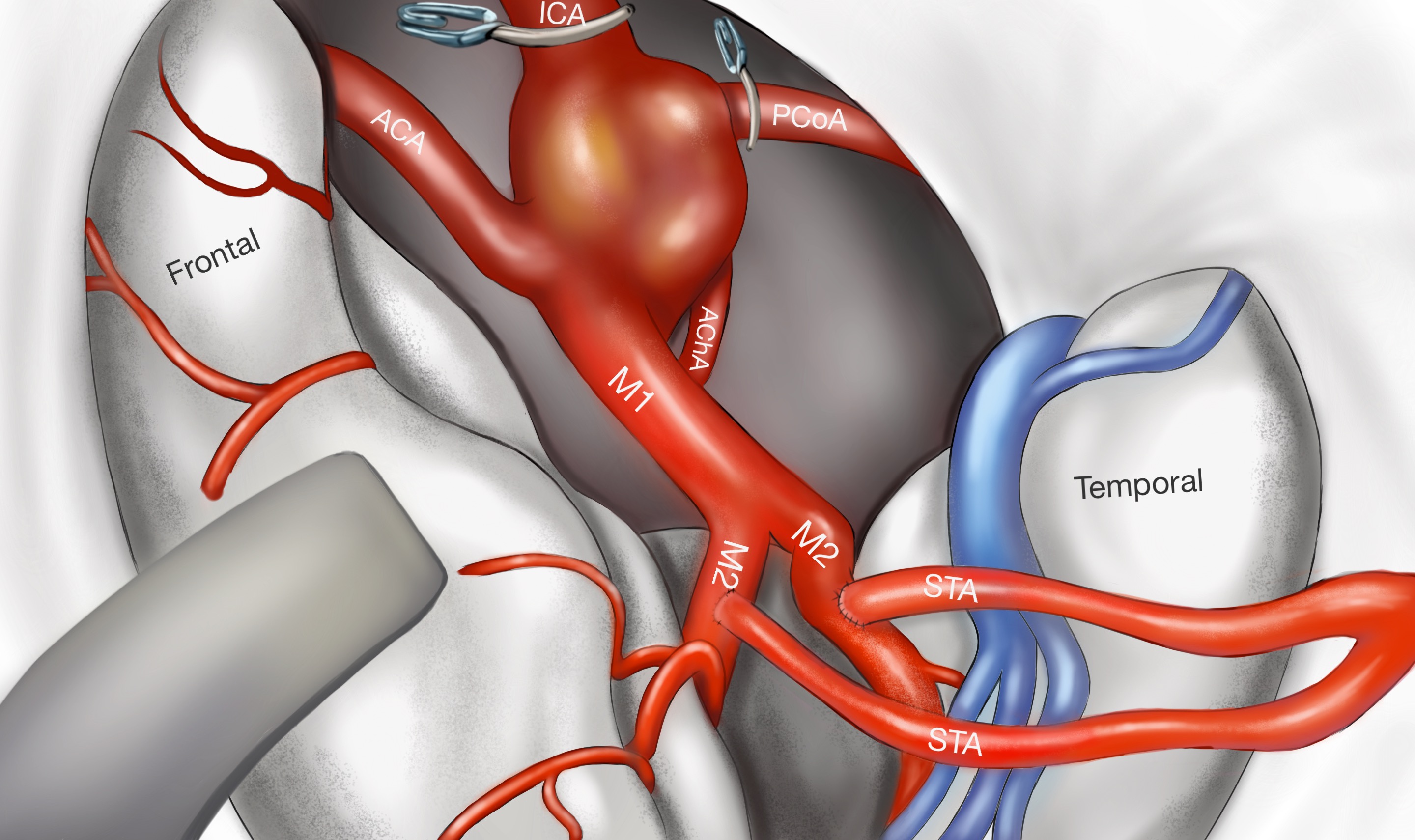
◆ Clipping
Surgical management of cerebral aneurysms, in which a clip is placed across the neck of the aneurysm, is an effective and safe procedure with the evolution of microsurgical techniques in the hands of an experienced surgeon. This applies to patients with unruptured cerebral aneurysms and those with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
You can find professional doctors and experts about this disease here for your further consultation and treatment.




Any use of this site constitutes your agreement to the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy linked below.
A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for noncommercial personal use only. "China-INI," "chinaini.org" are trademarks of China International Neuroscience Institute.
© 2008-2021 China International Neuroscience Institute (China-INI). All rights reserved.